Communication System Model
In this article I’m going to talk about Communication System Model in details include their 5 parts, (1) Source coding and decoding, (2) Encoding and decoding of channels, (3) Encryption and decryption, (4) Digital modulation and demodulation, (5) Synchronization. Let’s dive deep…
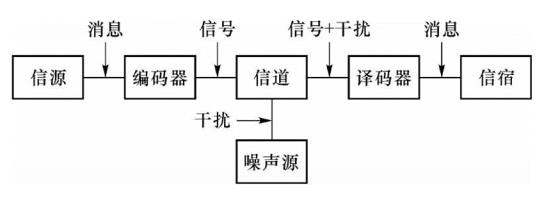
Analog Communication System Model
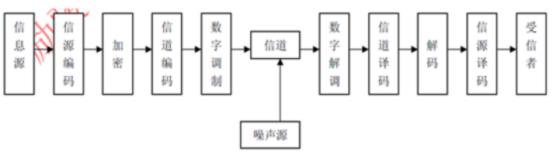
Digital Communication System Model
(1) Source coding and decoding:
Two basic functions: one is to improve the effectiveness of information transmission, that is, to reduce the number of symbols to reduce the rate of symbols through a certain compression coding technology. The second is to complete the analogue/digital (A/D) conversion. That is, when the information source gives an analogue signal, the source encoder converts it into a digital signal to realize the digital transmission of the analogue signal.
(2) Encoding and decoding of channels:
Function: To perform error control. Digital signals may be affected by noise and other errors during transmission. In order to reduce errors, the channel encoder and the transmitted information symbols add protection components (supervision symbols) according to certain rules to form the so-called “anti-interference coding.”. The channel decoder at the receiving end decodes based on the rules that are the opposite of those at the sending end. It finds errors or fixes them, which makes the communication system more reliable.
(3) Encryption and decryption:
In order to ensure the security of the transmitted information, the transmitted digital sequence is artificially scrambled—that is, a password is added. This process is called encryption. Restoring the original information is decryption.
(4) Digital modulation and demodulation:
Digital modulation: The spectrum of the digital baseband signal is shifted to higher frequencies to form a bandpass signal suitable for channel transmission. At the receiving end, the digital baseband signal can be restored using either coherent demodulation or non-coherent demodulation.
(5) Synchronization:
Synchronization: It is to keep the signals at both ends of the transceiver synchronized in time, and it is a prerequisite to ensure the orderly, accurate, and reliable operation of the digital communication system.
This is the article on the “Communication System Model” brought to you by Shenzhen HDV phoelectron Technology Co., Ltd. hope this article can help you to increase your knowledge. Besides this article if you’re looking for a good optical fiber communication equipment manufacturer company you may consider about us.
Shenzhen HDV phoelectron Technology Co., Ltd. is mainly a manufacturer of communication products. At present, the equipment produced covers the ONU series, optical module series, OLT series, and transceiver series. We can provide customized services for different scenarios. which can be used for different Provide the corresponding high-quality service according to the needs of users. You are welcome to consult.