Learn about fiber, single-mode fiber, and multi-mode fiber in one minute
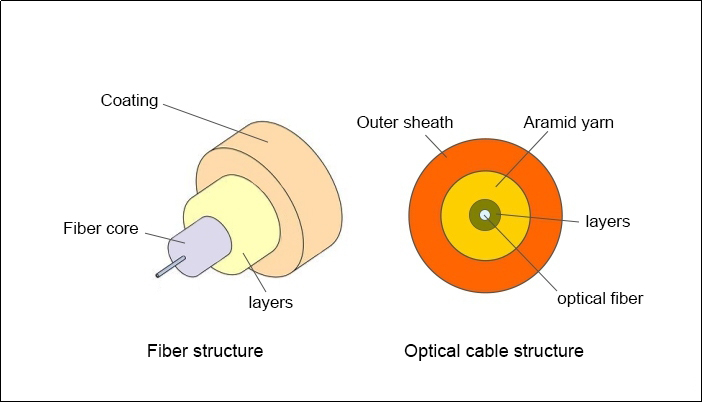
The basic structure of optical fiber
The bare fiber of optical fiber is usually divided into three layers: core, cladding and coating.
The fiber core and cladding are composed of glass with different refractive indexes, the center is a high refractive index glass core (germanium-doped silica), and the middle is a low refractive index silica glass cladding (pure silica). Light enters the fiber at a specific angle of incidence, and the total emission occurs between the fiber and the cladding (because the refractive index of the cladding is slightly lower than the core), so it can propagate in the fiber.
The main function of the coating is to protect the optical fiber from external damage, while increasing the flexibility of the optical fiber. As mentioned earlier, the core and cladding are made of glass and cannot be bent and fragile. The use of the coating layer protects and prolongs the life of the fiber.
A layer of outer sheath is added to the non-bare fiber. In addition to protecting it, the outer sheath of different colors can also be used to distinguish various optical fibers.
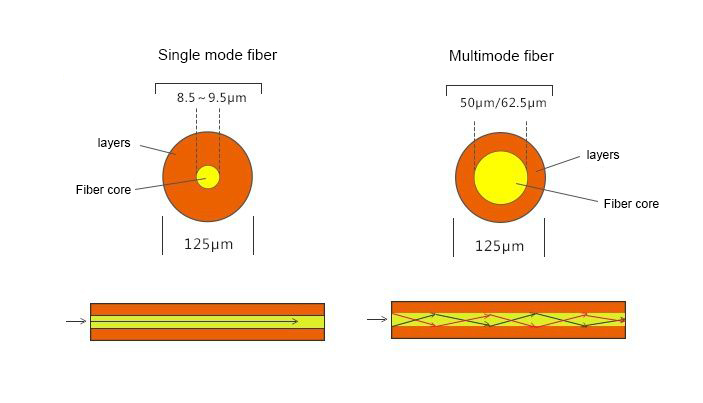
Optical fiber is divided into single mode fiber (Single Mode Fiber) and multimode fiber (Multi Mode Fiber) according to the transmission mode. Light enters the fiber at a specific angle of incidence, and full emission occurs between the fiber and the cladding. When the diameter is small, only one direction of light is allowed to pass through, that is, a single-mode fiber; when the fiber diameter is large, light can be allowed. Inject and propagate at multiple incident angles, this time it is called a multimode fiber.
Optical fiber transmission characteristics
Optical fiber has two main transmission characteristics: loss and dispersion. The loss of an optical fiber refers to the attenuation per unit length of the optical fiber, in dB/km. The level of optical fiber loss directly affects the transmission distance of the optical fiber communication system or the distance between the relay stations. Fiber dispersion refers to the fact that the signal transmitted by the fiber is carried by different frequency components and different mode components, and the transmission speeds of different frequency components and different mode components are different, which leads to signal distortion.
Fiber dispersion is divided into material dispersion, waveguide dispersion and modal dispersion. The first two kinds of dispersion are caused by the signal not being a single frequency, and the latter kind of dispersion is caused by the signal being not a single mode. The signal is not a single mode will cause mode dispersion.
Single-mode fiber has only one fundamental mode, so there is only material dispersion and waveguide dispersion, and no modal dispersion. The multimode fiber has inter-mode dispersion. The dispersion of the optical fiber not only affects the transmission capacity of the optical fiber, but also limits the relay distance of the optical fiber communication system.
Single mode fiber
Single-mode fiber (Single Mode Fiber), light enters the fiber at a specific incident angle, and full emission occurs between the fiber and the cladding. When the diameter is shortened, only one direction of light is allowed to pass through, that is, a single-mode fiber; The central glass core of the mode fiber is very thin, the core diameter is generally 8.5 or 9.5 μm, and it works at 1310 and 1550 nm wavelengths.
Multimode fiber
Multi-mode fiber (Multi Mode Fiber) is a fiber that allows multiple guided mode transmission. The core diameter of a multimode fiber is generally 50μm/62.5μm. Because the core diameter of a multimode fiber is relatively large, it can allow different modes of light to be transmitted on one fiber. The standard wavelengths of multimode are 850nm and 1300nm respectively. There is also a new multimode fiber standard called WBMMF (Wideband Multimode Fiber), which uses wavelengths between 850nm and 953nm.
Both single-mode fiber and multi-mode fiber have a cladding diameter of 125 μm.
Single-mode fiber or multi-mode fiber?
Transmission distance
The smaller diameter of the single-mode fiber makes the reflection tighter, allowing only one mode of light to travel, so that the optical signal can travel farther. As the light passes through the core, the amount of light reflections decreases, reducing attenuation and causing further signal propagation. Because it has no inter-mode dispersion or small inter-mode dispersion, single-mode fiber can transmit 40 kilometers or more without affecting the signal. Therefore, single-mode fiber is generally used for long-distance data transmission and is widely used in telecommunications companies and cable TV providers and universities, etc.
Multimode fiber has a larger diameter core and can transmit light in multiple modes. In multi-mode transmission, due to the larger core size, the inter-mode dispersion is larger, that is, the optical signal “spreads” faster. The signal quality will be reduced during long-distance transmission, so multi-mode fiber is usually used for short-distance, audio/video applications and local area networks (LANs), and OM3/OM4/OM5 multi-mode fiber can support high-speed data transmission.
Bandwidth, capacity
Bandwidth is defined as the ability to carry information. The main factor that affects the width of the optical fiber transmission band is various dispersions, of which modal dispersion is the most important. The dispersion of single-mode fiber is small, so it can transmit light in a wide frequency band for a long distance. Since multi-mode fiber will produce interference, interference and other complex problems, it is not as good as single-mode fiber in bandwidth and capacity. The latest generation of multi-mode fiber bandwidth OM5 is set to 28000MHz/km, while the single-mode fiber bandwidth is much larger.