Regarding fiber broadband technology, this article is enough!
Today, the Internet is an essential part of our daily lives. In fact, there are two main ways we use the Internet: one is through the mobile phone’s data service; the other, more generally, is through broadband at home or work.
From a professional perspective, wireless access is wireless access. By wired, it is wired access.
Obviously, mobile data services must be wireless. Broadband at home or work is wired.
Wired access is also often referred to as “fixed network access” (fixed network: fixed telephone network). Broadband access and IPTV access are all “cable.”
What I want to introduce today is broadband access.
Development history of broadband Internet access
Let’s start from the beginning.
Do you still remember when you first started online?
The earliest time to start surfing the Internet was in college. There is a telephone line in the dormitory. When you want to access the Internet, plug in your computer’s modem card, and then set up dial-up Internet on your computer.
After the settings are complete, start dialing.
After a creak of “heartbreak”, it shows that dialing has been successful, that is to connect to the Internet.
What is the speed of dial-up Internet access? 56Kbps … After a creaking sound of “Heartbroken Heart”, it shows that dialing has been successful, that is, the Internet connection.
What is the speed of dial-up Internet access? 56Kbps …
Yes, you read that right, it was so slow. At the beginning, our entire dormitory relied on this phone to dial up and connect to the school system to choose courses. At that time, please feel for yourself. . .
Moreover, with this original method, once you dial the Internet, the phone cannot be connected and is in a “busy” state. Not only that, the cost is also very expensive, and Internet access is charged on a minute-by-minute basis, just like calling. The speed is already slow. Seeing the money rush away can kill you suddenly.
Later, after a few years, ADSL started to be available. A gadget like the following picture appears, called ADSL cat (Modem), the phone line is plugged into the ADSL cat, and then the ADSL cat is connected to the computer through a network cable.
After using ADSL, the network speed has also been significantly improved, from 512Kbps to 1Mbps, and then to 2Mbps.
Although the rate is still low, it is much faster than 56K. The basics of accessing web pages are smooth, and the QQ chat is faster, and everyone’s Internet experience has been greatly improved.
This ADSL, which is Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line, is a type of DSL technology. DSL technology was invented in 1989 by Bell Communications Research Institute.
When ADSL first appeared, I was curious. It was also a thin telephone line, not a twisted pair of network cable. Why did the speed suddenly come up?
It turned out that the original telephone line, which we used to make calls, only took up the low-frequency part of the copper wire (the part below 4KHz) and did not fully realize its full potential.
The ADSL technology uses frequency division multiplexing to divide the ordinary telephone line into three relatively independent channels of telephone, uplink and downlink, which not only avoids interference but also increases the rate.
Specifically, ADSL uses DMT (Discrete Multi-Tone) technology to divide the original telephone line from the 4KHz to 1.1MHz frequency band into 256 subbands with a bandwidth of 4.3125KHz. Among them, the frequency band below 4KHz is still used to transmit POTS (traditional telephone service), the frequency band from 20KHz to 138KHz is used to transmit uplink signals, and the frequency band from 138KHz to 1.1MHZ is used to transmit downlink signals.
Compared with the original method, ADSL not only greatly increases the speed, but the price also drops significantly. When you go online, you no longer need to race against time. What’s more, Internet and phone calls no longer conflict, and can be performed simultaneously.
Later, on the basis of ADSL, ADSL2 and ADSL2 + were upgraded, and the rate was once reached 20Mbps.
In addition to ADSL, radio and television broadband (cable communication), ISDN dedicated lines and other Internet access methods have appeared around us.
Radio and television broadband, I believe that those who have used it are impressed. In fact, it is a way to provide broadband access through coaxial cable of cable television (CATV).
ISDN stands for Integrated Services Digital Network. The cost is relatively high, and the network speed is not fast.
In any case, although ADSL has greatly increased the network speed, the transmission rate of copper wires is ultimately limited. So, it is urgent to find an alternative.
As a result, optical fibers appeared around us, and the “optical communication era” came.
Optical communication era
Everyone must have heard of “light advance copper retreat”. The so-called “optical advance copper retreat” is, in popular terms, the gradual replacement of copper wires (telephone wires, coaxial cables, twisted pairs) with optical fibers to achieve the transition from narrow-band copper cable networks to fiber-optic broadband networks.
The reason for this is partly because of the demand for speed increase, and partly because of the cost.
With the development of the times, the price of copper metal has increased significantly, while the prices of optical fiber cables and optical transceiver modules have been decreasing year by year. As an operator, of course I like cheap and easy to use!
OK, let’s take a look at what this fiber broadband is.
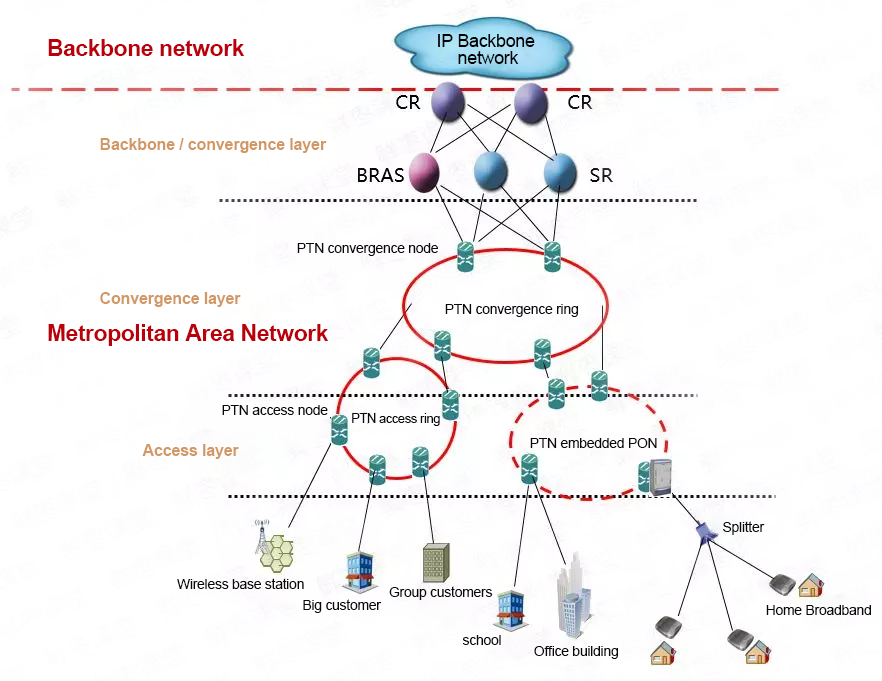
First, let’s look at an overall structure of the operator’s communication network:
At the top is the IP backbone network, which is simply the core network of the operator. The backbone network is connected to other operators. The backbone networks of different operators form the backbone of the Internet.
Moreover, it is also connected to other service networks, such as PSTN network (telephone network) and IPTV network, providing users with a variety of services.
Down the national backbone network, it is a provincial backbone network. Further down is the Metropolitan Area Network. As the name suggests, it is a communication network within the city.
The MAN is divided into three layers: the core layer, the convergence layer, and the access layer.
The access layer is the layer closest to our client. This part of the access network is also called the access network. The focus and difficulty of “light advance copper retreat” lies in this access layer.
At present, the most mainstream fiber access technology is PON.
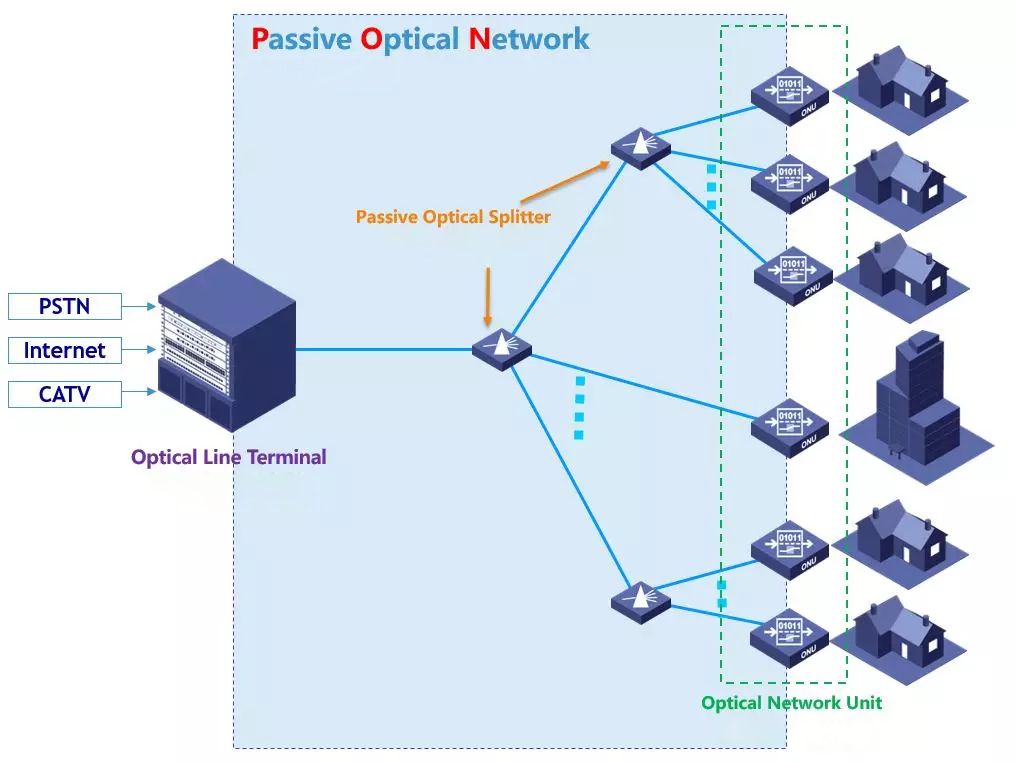
PON is Passive Optical Network, a passive optical network.
What is passive?
This “source” refers to the power source, energy source, and power source.
To put it plainly, an electronic device without such a “source” is called a passive device. To make it simpler, in a passive network, what you give is what you have, there is no energy source to zoom in or convert.
Compared with active optical network, the biggest advantage of passive optical network is that it reduces the failure rate. Active components are more prone to failure points.
The network architecture of PON is as follows:
PON is composed of the following parts:
OLT (Optical Line Terminal)
On the one hand, the signals carrying various services are aggregated at the central office, and sent to the access network according to a certain signal format for transmission to the end user. On the other hand, the signals from the end user are sent to the various service networks according to the service type. in.
POS (passive optical splitter)
This is easy to understand, that is to distribute downlink data and aggregate uplink data.
ONU (Optical Network Unit) / ONT (Optical Network Terminal)
Device closest to the user. Many people can’t distinguish between ONU and ONT. In fact, a simple distinction is that ONT is a type of ONU. ONT has only one port and serves one user. ONU serves multiple users. The light cat in our family is ONT.
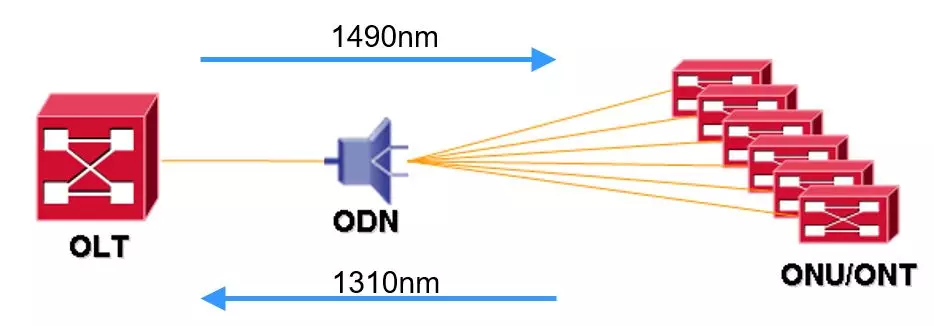
PON uses WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing, which is actually frequency division multiplexing, wavelength × frequency = speed of light) technology to achieve single-fiber bidirectional transmission with an upstream wavelength of 1310nm and a downstream wavelength of 1490nm.
PON has many advantages such as high bandwidth, high efficiency, large coverage, and rich user interfaces. It is currently the most popular optical access technology.
According to the content of the bearer, PON is mainly divided into the following types:
- ATM-based Passive Optical Network (APON)
- Ethernet (EPON) based Ethernet passive optical network (EPON)
- Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) based on GFP (General Framing Procedure)
In fact, you don’t have to remember so much. Anyway, remember that GPON is the best and the best. Now all major operators are working hard to develop GPON.
Graphical fiber-optic Internet access process
After speaking for a long time, everyone may feel a little dizzy, let’s use actual cases and pictures to illustrate it.
We start from the IP backbone network, from top to bottom, one by one.
First of all, the so-called Internet access is to enjoy the services provided by network service providers. For example, use WeChat service provided by Tencent, Taobao service provided by Ali, and video service provided by Youku.
These services are based on enterprises’ servers in the data center.
If it is an enterprise data center, there will be connection lines from different operators. Through these lines, connect to the national IP backbone network of the operator.
The national backbone network is then connected to the provincial backbone network. Provincial backbone network, and then connect to the metropolitan area network of the city. After these forwarding through the bearer network, finally came to the access network. That is our PON.
After arriving at the PON, the first step is to access the OLT.
The OLT is responsible for a certain area, a building or a residential area. This is based on the number and size of users. For densely populated areas like office buildings or schools, it may also be placed directly inside the building.
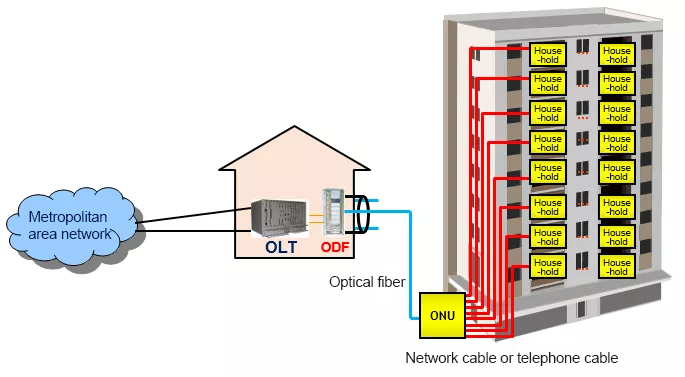
The optical fibers from the OLT equipment are connected to various residential buildings in the community through ODF racks and optical delivery boxes.
In the residential building elv well, tend to have a light tap box, inside the beam splitter.
The optical splitter can divide a fiber into multiple channels according to the ratio of 1:16 or 1:32, covering users on the corresponding floor (or multiple floors).
The optical fibers from the splitter enter the homes of the residents.
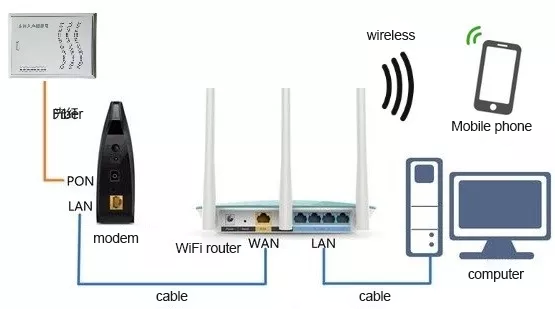
After the fiber is entered, it will be connected to the weak current box in the home.
There will be a “light cat” in the low-voltage box. This optical cat, as mentioned before, is actually an ONT, a passive optical fiber user access device.
The next part is very familiar to everyone, every family will buy a wireless router (that is, Wi-Fi router). Through the router, connect the optical cat to dial, and change the optical fiber network signal into your home’s wireless network signal, so that mobile phones, computers, iPads and other devices can access the Internet.
The above is the most typical optical fiber broadband access method.
Everyone noticed that in the above case, the optical fiber is directly connected to the home, this is called FTTH (Fiber To The Home).
However, for many old communities, the basic network equipment is not enough to meet the conditions of FTTH. If the fiber cannot reach the home, FTTB or FTTC will be adopted.
FTTB: Fiber To The Building
FTTC: Fiber To The Curb
Taking FTTB as an example, when the optical fiber from the OLT passes through the ODF optical distribution frame and splitter, when it arrives in the building, it directly enters the ONU in the weak current room of the building.
ONU has a variety of access methods. Simply put, it is to change the optical fiber method to ADSL method, POTS method, and LAN method.