What is an optical splitter and what are the important technical indicators?
The optical splitter is one of the important passive devices in the optical fiber link, and mainly plays the role of splitting. It is generally used in the optical line terminal OLT and the optical network terminal ONU of the passive optical network to realize the optical signal splitting.
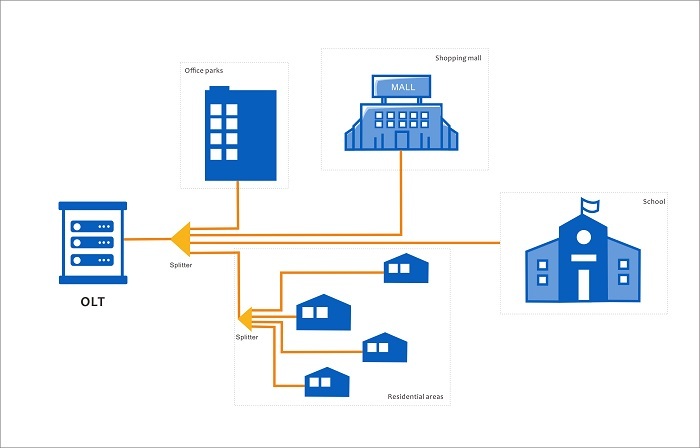
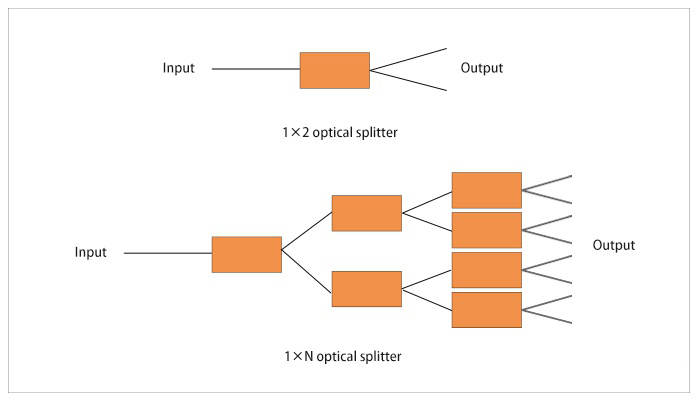
The optical splitter distributes the transmitted optical signal in one optical fiber to multiple optical fibers. There are many types of distribution, 1 × 2, 1 × 4, 1 × N, or 2 × 4, M × N. The general architecture of FTTH is: OLT (computer room office end)-ODN (passive optical network distribution system)-ONU (user end), in which the optical splitter is applied in ODN to realize that multiple end users share one PON interface. In the PON structure, when the distribution of buildings is scattered and irregular, such as the distribution of villas, the distance is far, and the density of users is low, the centralized splitting method can make full use of resources and cover the surrounding.
Only one optical splitter may be used in a passive optical network, or multiple optical splitters may be used together to split optical signals.
The performance indicators that affect the optical splitter are generally the following:
Insertion loss
The insertion loss of the fiber splitter refers to the number of dB of each output relative to the input optical loss. Generally speaking, the smaller the insertion loss value.
Split ratio
The split ratio is defined as the output power ratio of each output port of the fiber splitter. Generally, the splitting ratio of the PLC optical splitter is evenly distributed, and the splitting ratio of the fused tapered optical splitter can be unequal. The specific ratio setting of the splitting ratio is related to the wavelength of the transmitted light. For example, when an optical branch transmits 1.31 micron light, the splitting ratio of the two output ends is 50:50; when transmitting 1.5μm light, it becomes 70: 30 (The reason why this happens is because the fiber splitter has a certain bandwidth, that is, the bandwidth of the optical signal transmitted when the split ratio is basically unchanged).
Isolation
Isolation refers to the isolation capability of one optical path of an optical fiber splitter from optical signals in other optical paths.
Return loss
Return loss, also called reflection loss, refers to the power loss of the optical signal returned or reflected by the discontinuity in the fiber or transmission line. The greater the return loss, the better, to reduce the impact of reflected light on the light source and system.
In addition, uniformity, directivity, PDL polarization loss, etc. are also parameters that affect the performance of the optical splitter. Optical fiber splitter is one of the most important passive devices in the optical fiber link, and is especially suitable for connecting MDF and terminal equipment in passive optical networks (EPON, GPON, BPON, FTTX, FTTH, etc.) to distribute optical signals.