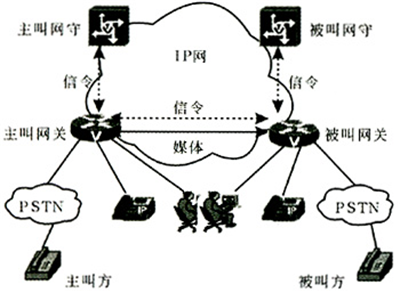
Basic transmission process of VoIP
Traditional telephone network is voice by circuit exchange, the required transmission broadband of 64kbit/s. The so-called VoIP is the IP packet exchange network as the transmission platform, the simulated voice signal compression, packaging and a series of special processing, so that it can use the unconnected UDP protocol for transmission.
Several elements and functions are required to transmit voice signals on an IP network. The simplest form of the network consists of two or more devices with VoIP capabilities that are connected via an IP network.
1.Voice-Data Transformation
Voice signal is analog waveform, through IP to transmit voice, whether real-time application business or real-time application business, first to voice signal analog data conversion, namely the analog voice signal 8 or 6 quantification, and then sent to the buffer storage, the size of the buffer can be selected according to the requirements of the delay and coding. Many low bit rate encoders are encoded in frames.
Typical frame length ranged from 10 to 30 ms. Considering the costs during transmission, interlingual packets usually consists of 60, 120, or 240ms of speech data. Digitization can be implemented using various voice coding schemes, and the current voice coding standards are mainly ITU-T G.711. The voice encoder at the source destination must implement the same algorithm so that the speech device at the destination can restore the analog speech signal.
2.Original data-to-IP conversion
Once the speech signal is digitally coded, the next step is to compress encode the speech packet with a specific frame length. Most of the encoders have a specific frame length. If an encoder uses 15ms frames, the 60ms package from the first place is divided into four frames and encoded in sequence. Each frame has 120 speech samples (sampling rate of 8kHz). After encoding, the four compressed frames were synthesized into a compressed speech package and sent to the network processor. The network processor adds a Baotou, time scale, and other information to the voice and passes it to the other endpoint through the network.
The speech network simply establishes a physical connection between the communication endpoints (one line) and transmits the encoded signals between the endpoints. Unlike circuit switching networks, IP networks do not form connections. It requires that data be placed in variable long data reports or packets, then address and control information to each datagram and sent over the network, forwarded to the destination.
3.Transfer
In this channel, the entire network is viewed as a voice packet received from the input and then transmitted to the network output within a certain time (t). The t can vary in a full range, reflecting the jitter in the network transmission.
The same node in the network checks the addressing information associated with each IP data and uses this information to forward that datagram to the next stop on the destination path. A network link can be any topology or access method that supports IP data streams.
4.The IP package- -the transformation of the data
The destination VoIP device receives this IP data and starts processing. The network level provides a variable length buffer used to regulate the jitter generated by the network. The buffer can accommodate many voice packets, and users can choose the size of the buffer. Small buffers produce less latency, but do not regulate large jitter. Second, the decoder uncompresses the encoded speech packet to produce a new speech package, and this module can also operate by frame, exactly the same length as the decoder.
If the frame length is 15ms, the 60ms voice packets are divided into 4 frames, and then they are decoded back to a 60ms voice data flow and sent to the decoding buffer. During the processing of the data report, the addressing and control information is removed, the original original data is retained, and this original data is then provided to the decoder.
5.Digital speech was converted to analog speech
The playback drive removes the voice samples (480) in the buffer and sends them to the sound card through the speaker at a predetermined frequency (e. g. 8kHz). In short, the transmission of voice signals on the IP network goes through the conversion from analog signal to digital signal, digital voice packaging into an IP packet, IP packet transmission through the network, IP packet unpacking and the restoration of digital voice to the analog signal.
Second, VoIP-related technical standards
For multimedia applications on existing communication networks, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU-T) has developed the H.32x Multimedia communication series protocol, the following main standards for a simple description:
H.320, Standard for multimedia communication on the narrowband video telephone system and terminal (N-ISDN);
H.321, Standard for multimedia communication on the B-ISDN;
H.322. Standard for multimedia communication on the LAN guaranteed by QoS;
H.323. Standard for multimedia communication on a packet switching network without QoS guarantee;
H.324, a standard for multimedia communication on low bit rate communication terminals (PSTN and wireless network).
Among the above standards, H. The 323 Standard-defined networks are the most widely used, such as Ethernet, Token Network, FDDI Network, etc.because of H.The application of 323 standard has naturally become a hot spot in the market, so below we will focus on H.323。H.323 Four main components are defined in the proposal: terminal, gateway, gateway management software (also known as gateway or gate), and multi-point control unit.
1.Terminal (Terminal)
All terminals must support voice communication, and the video and data communication capabilities are optional.all H.The 323 terminal must also support the H.245 Standard, H.245 The standard is used to control the channel usage and the channel performance.H.323 The main parameters of the speech codec in voice communication are specified as follows: ITU recommended voice bandwidth / KHz transmission bit rate / Kb/s compression algorithm annotation G.711 3.4 56,64 PCM simple compression, applied to the PSTN in G.728 3.4 16 LD-CELP voice quality as G.711, as applied to the low-bit-rate transmission G.722 7 48,56,64 ADPCM voice quality is higher than G.711, applied to high bit rate transmission G.723.1G.723.0 3.4 6.35.3 LP-MLQ Voice quality is acceptable, G.723.1 Adopt a G for the VOIP forum.729G.729A 3.4 8 CS-ACELP delay is lower than G.723.1, Voice quality is higher than the G.723.1。
2.Gateway (Gateway)
This is H.An option for the 323 system.The gateway can transform the protocols, audio, video coding algorithms and control signals used by different systems to accommodate the system terminal communication.Such as the PSTN-based of H.324 System and narrowband ISDN-based H.The 320 System and the H.323 For system communication, it is necessary to configure the gateway;
3.Customs keeping (Gatekeeper)
This is H.An optional component of the 323 system is the software to complete the management function.It has two main functions: the first is to the H.323 Application management; the second is the management of the terminal communication through the gateway (such as call establishment, removal, etc.).Managers can perform address conversion, bandwidth control, call authentication, call recording, user registration, communication domain management and other functions through customs keeping.one H.323 The communication domain can have multiple gateways, but only one gateway works.
4.Multipoint control unit (Multipoint Control Unit)
The MCU enables multi-point communication on an IP network, and point-to-point communication is not required.The whole system forms a star topology through the MCU.The MCU contains two main components: multipoint controller MC and multipoint processor MP, or without MP.H between MC processing terminals.245 Control information to build a minimal public namer for audio and video processing.MC does not directly process any media information stream, but leaves it to MP.The MP mixes, switches, and processes the audio, video, or data information.
In the industry there are two parallel architectures, one is the ITU-T H introduced above.323 Protocol is the SIP protocol (RFC2543) proposed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), and the SIP protocol is more suitable for intelligent terminals.
Third, The impetus for VoIP development
The widespread use of VoIP will quickly come true due to many hardware, software, related developments and technological breakthroughs in the protocol and standards.Technological advances and developments in these fields play a driving role in creating a more efficient, functional and interoperable VoIP network.The technical factors that promote the rapid development and even widespread application of VoIP can be summarized into the following aspects.
1.Digital Signal Processor
Advanced digital signal processors (Digital Signal Processor, DSP) perform the computation-intensive components required for voice and data integration.DSP processes digital signals primarily to perform complex calculations that may otherwise have to be performed by a universal CPU.The combination of their specialized processing power with the low cost makes the DSP well suited to perform the signal processing functions in the VoIP system.
Single voice stream on the G.729 The computing cost of voice compression is usually large, requiring 20MIPS. If a central CPU is required to perform routing and system management functions while processing multiple voice streams, this is unrealistic. Therefore, using one or more DSP can uninstall the computing task of the complex voice compression algorithm from the central CPU.In addition, DSP is suitable for voice activity detection and echo cancellation, allowing them to process voice data streams in real time and quickly access on-board memory, so.In this section, we detail how to implement voice coding and echo cancellation on the TMS320C6201DSP platform.
Protocol and standard software and hardware H.323 Weighted fair queuing method DSP MPLS tag exchange weighted random early detection advanced ASIC RTP, RTCP dual funnel general cell rate algorithm DWDM RSVP rated access fast rate SONET Diffserv, CAR Cisco fast forwarding CPU processing power G.729, G.729a: CS-ACELP Extended Access Table ADSL, RADSL, SDSL FRF.11/FRF.12 Token barrel algorithm Multilink PPP Frame Relay Data rectifier SIP based on priority integration of CoS Packet over SONET IP and ATM QoS / CoS
2.Advanced dedicated integrated circuits
The Application-Specific Integrated Circait (ASIC) development has produced a faster, more complex, and more functional ASIC.ASIC is a specialized application chip that performs a single application or a small set of functions.Because they focus on very narrow application goals, they can be highly optimized for specific functions, usually with a dual-purpose CPU one or several orders of magnitude faster.
Just as the Thin Instruction set Computer (RSIC) chip focuses on quick execution of limit numbers, the ASIC is preprogrammed to perform a finite number of functions faster.Once development is completed, the cost of ASIC mass production is low, and it is used for network devices including routers and switches, performing functions such as routing table checking, group forwarding, group sorting and checking, and queuing.The use of ASIC gives the device higher performance and less cost.They provide increased broadband and better QoS support for the network, so they play a great role in promoting VoIP development.
3.IP transmission technology
Most transmission telecom networks use time-division multiplexing, while the Internet must adopt statistical reuse and long packet exchange. Compared, the latter has high utilization rate of network resources, simple and effective interconnection, and very applicable to data services, which is one of the important reasons for the rapid development of the Internet.However, broadband IP network communication requires QoS and delay characteristics, so the development of statistical multiplexing packet exchange has attracted concerned.At present, in addition to the new generation of IP protocol-IPV6, the world Internet engineering task group (IETF) proposed the multi-protocol tag exchange technology (MPLS), this is a kind of network layer selection based various tag / label exchange, can improve the flexibility of road selection, expand network layer selection ability, simplify the router and channel exchange integration, improve network performance.MPLS can work as an independent routing protocol, and compatible with the existing network routing protocol, support various operation, management and maintenance functions of IP network, make the QoS, routing, signaling performance greatly improved, to reach or near the level of statistical reuse fixed length packet exchange (ATM), and simple, efficient, cheap and applicable than ATM.
IETF is also locally grasping the new grouping technology, in order to achieve QoS road selection.The “tunnel technology” is being studied to achieve broadband transmission of one-way links.In addition, how to choose the IP network transmission platform is also an important field of research in recent years, and IP over ATM, IP over SDH, IP over DWDM and other technologies have appeared successively.
The IP layer provides IP users with high-quality IP access services with certain service guarantees.The user layer provides the access form (IP access and broadband access) and the service content form.In the basic layer, Ethernet, as the physical layer of the IP network, is a matter of course, but IP overDWDM has the latest technology, and has great potential for development.
Dense Wave Division MultipLexing (DWDM) injects new life into fiber networks and provides amazing bandwidth in telecom companies laying new fiber backbone.DWDM technology utilizes the capabilities of optical fibers and advanced optical transmission equipment.The name of wave division multiplexing is derived for transmitting multiple wavelengths of light (LASER) from a single stream of optical fiber.Current systems can send and recognize 16 wavelengths, while future systems can support 40 to 96 full wavelengths.This is significant because each additional wavelength adds an additional flow of information.You can therefore expand the 2.6 Gbit/s (OC-48) network by 16 times without having to lay new fibers.
Most new fiber networks run OC-192 at (9.6 Gbit/s), generating capacity over 150 Gbit/s on a pair of fibers when combined with DWDM.In addition, DWDM provides interface protocol and speed-independent features, and supports both ATM, SDH and Gigabit Ethernet signal transmission on a single fiber, which can be compatible with the existing networks, so DWDM can protect existing assets, but also provide ISP and telecom companies with stronger backbone, and make broadband less expensive and more accessible, which provides strong support for the bandwidth requirements of VoIP solutions.
The increased transmission rate can not only provide a coarser pipeline with less chance of blocking, but also reduce the delay by much, and thus can greatly reduce the QoS requirements on IP networks.
4.Broadband access technology
User access of IP network has become a bottleneck restricting the development of the whole network.In the long term, the ultimate goal of user access is fiber-to-home (FTTH).Broadly speaking, optical access network includes optical digital loop carrier system and passive optical network.The former is mainly in the United States, combined with open mouth V5.1/V5.2, transmitting its integrated system on optical fiber, showing great vitality.
The latter is mainly in the order and in Germany.For more than a decade, Japan has taken a series of measures to reduce the cost of passive optical network to a level similar to copper cables and metal twisted pair, and used it use.Especially in recent years, ITU has proposed the ATM-based passive optical network (APON), which complements the advantages of ATM and passive optical network. The access rate can reach 622 M bit/s, which is very beneficial to the development of broadband IP multimedia service, and can reduce the failure rate and the number of nodes, and expand the coverage.At present, ITU has completed the standardization work, manufacturers are actively developing, there will be goods on the market, will become the main development direction of broadband access technology for the 21st century.
At present, the main access technologies are: PSTN, IADN, ADSL, CM, DDN, X.25 and Ethernet and broadband wireless access system column, etc.These access technologies have their own characteristics, including the fastest developing ADSL and CM; CM (Cable Modem) uses coaxial cable, high transmission rate, strong anti-interference ability; but not two-way transmission, no uniform standard. ADSL (Asymmetrical Digital Loop) has exclusive access to broadband, making full use of the existing phone network and providing asymmetric transmission rate. The download rate on the user side can reach 8 Mbit/s, and the upload rate on the user side can reach 1M bit / s.ADSL provides the necessary broadband for businesses and all users, and greatly reduces costs.Using lower-cost ADSL regional circuits, companies now access Internet and Internet-based VPN at higher speeds, allowing higher VoIP call capacity.
5.Central processing unit technology
Central processing units (CPU) continue to evolve in function, power, and speed.This enables widespread application of multimedia PC and improves the performance of system functions limited by CPU power.The PC’s ability to process stream audio and video data has long been awaited by users, so delivering voice calls on data networks is naturally the next goal.This computing feature enables both advanced multimedia desktop applications and advanced features in network components to support voice applications.