Detailed EPON technology
First, what problem is the PON used to solve?
● With the emergence of high-bandwidth services such as video on demand, online games and IPTV, users are in urgent need of increasing access bandwidth.Existing ADSL-based broadband access methods are increasingly difficult to meet user requirements for high bandwidth, two-way transmission capability, and security.
● Due to the long transmission distance, strong anti-interference ability and large capacity, the optical fiber has been widely used in the backbone network. In recent years, with the decrease of the cost of the optical device, the optical fiber has gradually become the first choice for the transmission medium of the access network.
● Passive Optical Network (PON) is relatively low cost in fiber access mode and can be upgraded smoothly. It is increasingly favored by telecom operators and is considered to be an ideal solution to solve the “last mile” problem.
Second, the composition of the PON
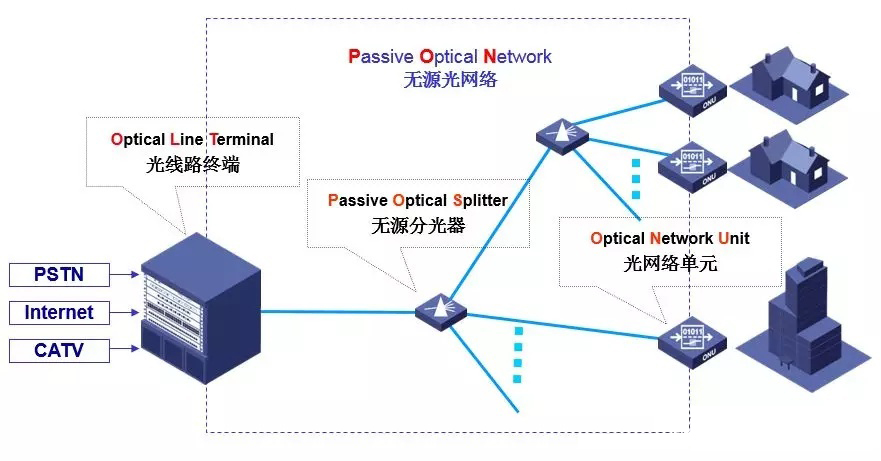
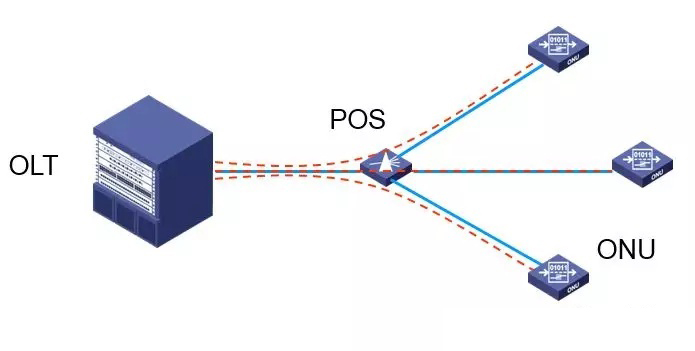
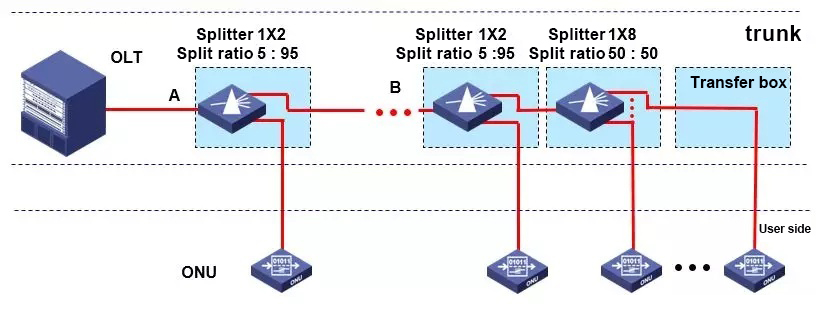
The PON consists of three parts: an optical line termination (OLT), an optical network unit (ONU), and a passive optical splitter (POS).
PON is an asymmetric, point-to-multipoint (P2MP) structure. The roles played by the OLT and the ONU are different. The OLT is equivalent to the role of the Master, and the ONU is equivalent to the role of the Slave.
Third, the advantages of PON:
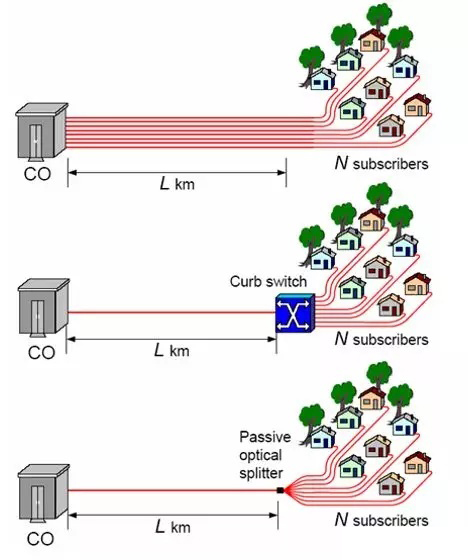
● Saving
P2P – N optical fibers; 2N optical transceiver
P2PCurb – 1 fiber; 2N+2 optical transceiver; requires local power supply; saves a lot of fiber
P2MP (PON) – 1 fiber; N+1 optical transceiver; a large number of optical fibers saved; a large number of optical transceivers
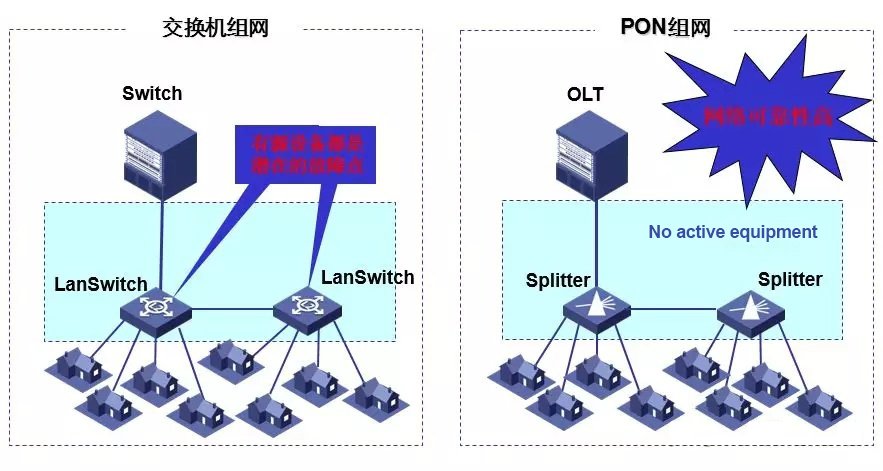
● Reliable
The signal does not pass through the active electronic device during the PON transmission process, greatly reducing the potential point of failure;
The use of passive devices simplifies the network hierarchy, and the flattened network structure is easier to maintain and manage.
● Long distance
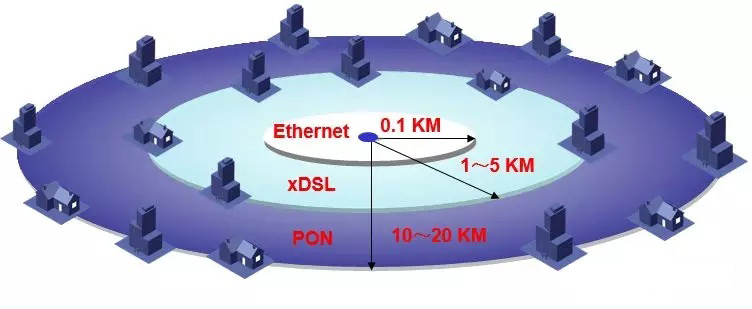
The PON transmission distance is 10 to 20km, which completely overcomes the limitation of the distance between Ethernet and xDSL access methods, and greatly enhances the flexibility of the operator’s end office deployment.
● High bandwidth
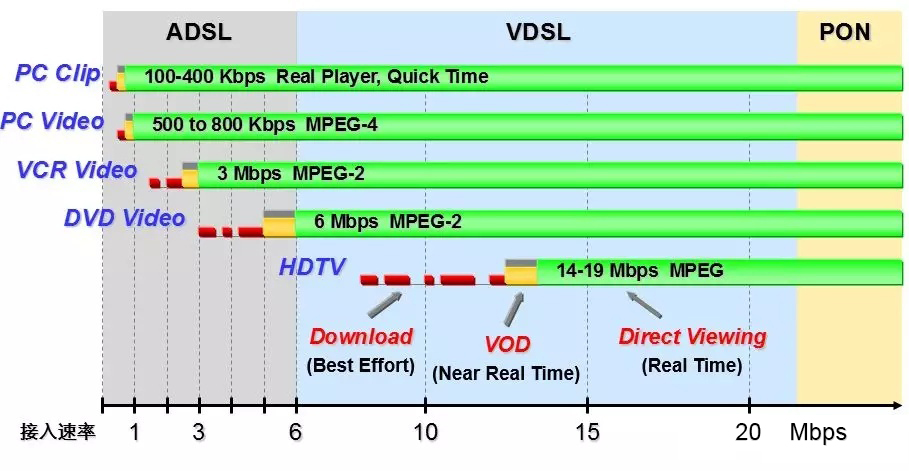
Compared with xDSL, PON has higher bandwidth and fully meets the needs of future HDTV online broadcast services.
● Flexible
The PON networking model is not limited, and the network of tree and star topology can be flexibly built.
The PON is especially suitable for occasions where the user access information points are scattered, and a trunk optical fiber can satisfy the access of all users to access information points.
Fourth, the main standard of PON
● GPON – GigabitPON, ITUG.984 protocol standard, upgrade and extension of APON, using a common frame format to provide support for a variety of services. The maximum rate is 2.5Gbps. GPON has advantages in high speed and support for multiple services, but the technology is complex, the cost is high, and the maturity of the product is not high.
● EPON——Ethernetover PON, IEEE802.3ah protocol standard, which transmits Ethernet format packets on the PON network and can support 1.25Gbps symmetric rate. EPON is based on Ethernet technology and the protocol is simple and efficient. Compared with APON, GPON has obvious advantages in terms of cost.
Fifth,Key technologies of EPON
● Channel multiplexing
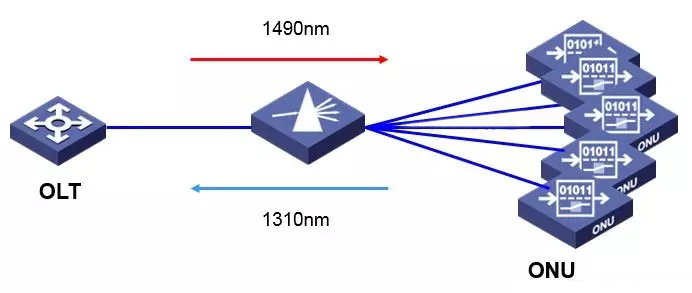
The EPON system adopts WDM technology to realize single-fiber bidirectional transmission;
The channel rate is 1.25 Gbps upstream and downstream.
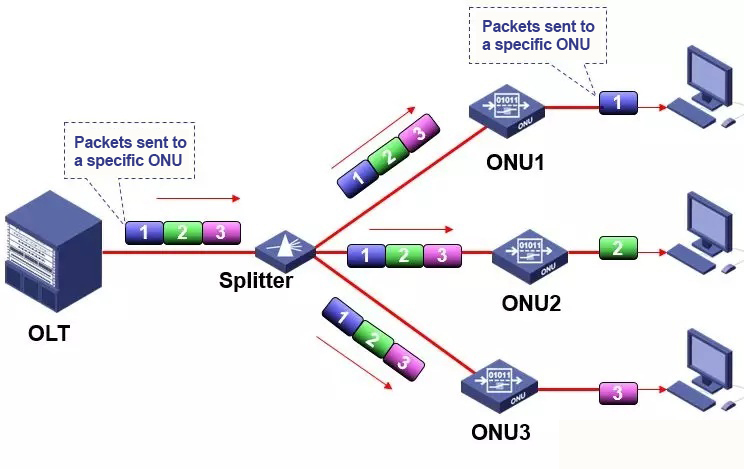
● EPON downlink transmission mode – broadcast mode
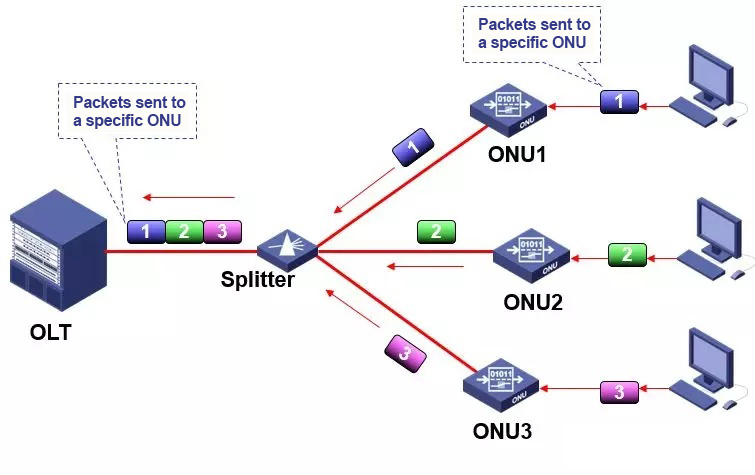
● EPON uplink transmission mode – TDMA mode
● Multipoint Control Protocol – MPCP
Unlike the Ethernet P2P architecture, PON is a P2MP architecture. The ONU competes for uplink channel resources, and an arbitration mechanism is needed to avoid uplink data collisions and to properly allocate channel resources. The 802.3ah protocol specifies the corresponding control protocol, the Multi-point MAC Control Protocol (MPCP);
lMPCP mainly defines a Multi-point MAC Control sublayer to extend and replace the MAC Control sublayer defined by the 802.3 protocol. The control frame of the MPCP protocol has a higher priority than the MACClient data frame.
● Ranging and delay compensation
The EPON uplink transmission adopts the TDMA mode. The OLT determines the time for the ONU to send data. Since each ONU is different from the OLT, there will be a delay difference. If there is no effective delay compensation mechanism, the uplink data transmission conflict will still occur.
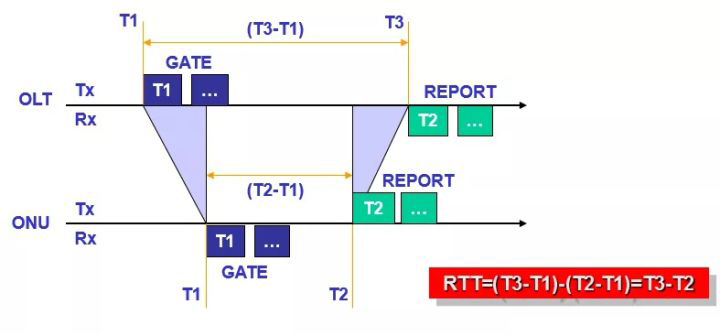
EPON ranging and delay compensation are the key technologies for uplink channel multiplexing. Ø In the DiscoveryProcessing process, the OLT calculates the RTT (RoundTrip Time) value of each ONU by measuring the newly registered ONU.
The OLT uses RTT to adjust the authorization time of each ONU.
The OLT can also initiate ranging when it receives an MPCP PDU.
RTT calculation:
The GATE frame contains a “timestamp” field that the ONU uses to refresh the local time register. The OLT can calculate the RTT through the received REPORT frame to perform experimental compensation.
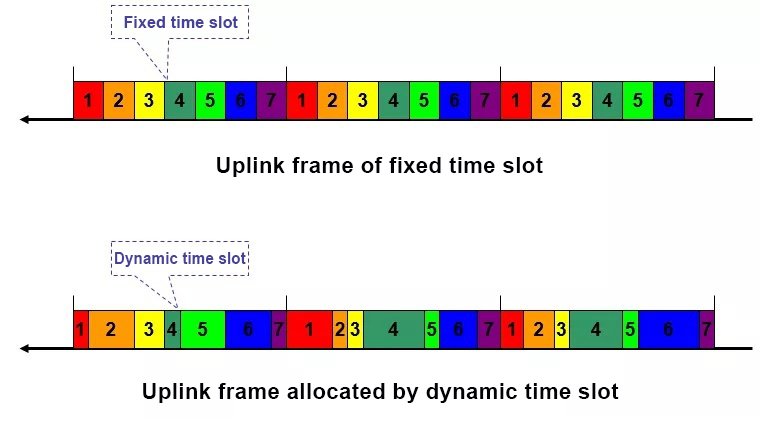
● Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA)
Comparison of fixed time slots and dynamic time slots: